
Many people ask if the tip42c can take the place of the tip41c in a circuit. The answer is no. The tip41c and tip42c are complementary types. The tip41c transistor is an NPN device. The tip42c is a complementary pnp transistor. Each transistor has its own job in circuits. The tip41c lets current flow one way. The tip42c lets current flow the other way. Picking the right transistor makes sure the circuit works right. This guide gives simple help for beginners. It explains the tip41c and how it is different from other transistors.
Key Takeaways
-
TIP41C is an NPN transistor. TIP42C is a PNP transistor. They work in opposite ways. You cannot swap them with each other.
-
Both transistors have similar voltage, current, and power ratings. They are good for power circuits if used the right way.
-
Using the wrong transistor type can make the circuit not work. It can break parts or cause safety problems. Always use the right transistor for your circuit.
-
TIP41C and TIP42C often work together in push-pull amplifier circuits. This helps the circuit work better and keeps current balanced.
-
Always check the datasheet for pinout, voltage, current, and gain. Do this before using or changing these transistors. This keeps everything safe and working right.
TIP41C vs TIP42C
Polarity and Type
The tip41c and tip42c are both power transistors. They have different polarities. The tip41c is an NPN transistor. The tip42c is a PNP transistor. This difference changes how they work in circuits.
| Feature | TIP41C (NPN) | TIP42C (PNP) |
|---|---|---|
| Transistor Type | NPN | PNP |
| Polarity/Channel Type | NPN (handles positive voltages) | PNP (handles negative voltages) |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage | Up to +100V | Up to -100V |
| Max Collector Current | +6A | -6A |
| Max Power Dissipation | 65W | 65W |
| Package Type | TO-220 | TO-220 |
| Complementary Pairing | Complement to TIP42C | Complement to TIP41C |
The tip41c lets current move from collector to emitter. This happens when a small current goes into the base. The tip42c works the other way. It lets current go from emitter to collector when the base is low. These two are called complementary. Many circuits use both for push-pull or amplifier outputs.
Note: Picking the right polarity matters a lot. If you use the wrong one, the circuit might not work.
Electrical Specs
Both tip41c and tip42c have close electrical ratings. Each can handle up to 100 volts between collector and emitter. Both can let 6 amps of current flow. Each can also get rid of up to 65 watts of heat. These numbers make them good for power jobs.
| Parameter | Rating |
|---|---|
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce) | 100 Volts |
| Maximum Collector Current (Ic) | 6 Amps |
| Peak Power Dissipation | 65 Watts |
Current gain, or hFE, is another important thing. Both tip41c and tip42c have a current gain from 15 to 75. This means they can make the input current up to 75 times bigger. Their current gain is close, so they work well together in circuits.
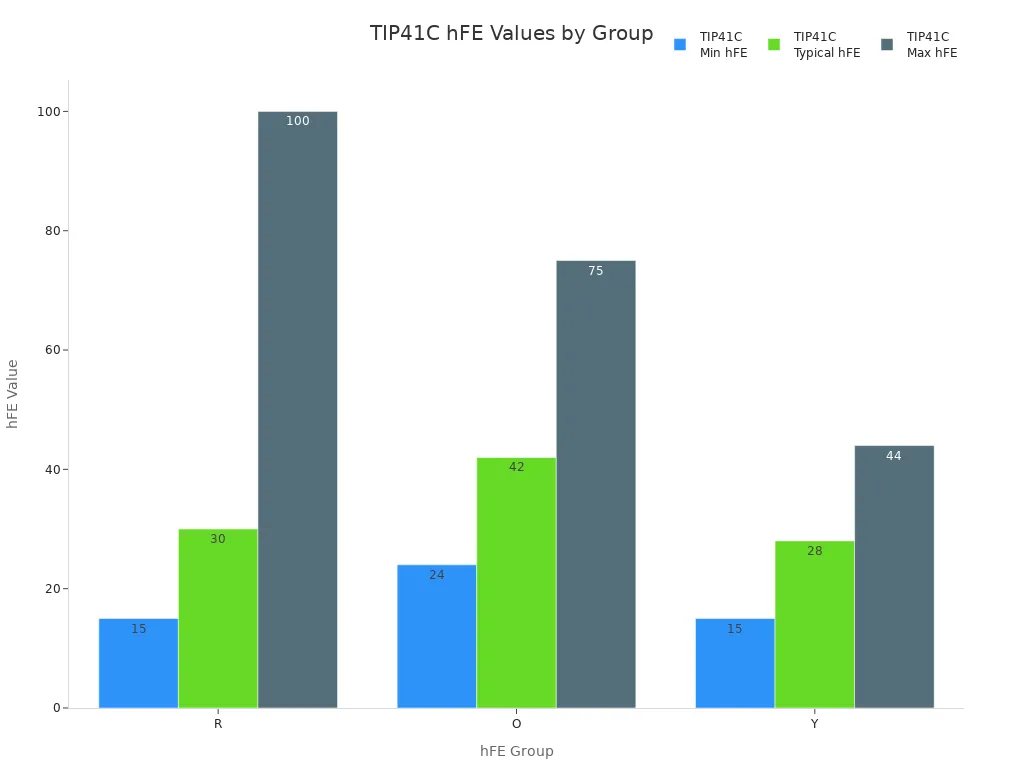
Here is a table showing current gain for different groups of tip41c and tip42c:
| Transistor | hFE Group | Minimum hFE | Typical hFE | Maximum hFE | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIP41C | R | 15 | 30 | 100 | Ic = 3A, Vce = 4V |
| TIP41C | O | 24 | 42 | 75 | Ic = 3A, Vce = 4V |
| TIP41C | Y | 15 | 28 | 44 | Ic = 3A, Vce = 4V |
| TIP42C | R | 15 | (similar) | (up to 75) | Ic = 3A, Vce = 4V |
Both transistors have matching current gain. This helps make balanced circuits.
TIP41C Pinout
The tip41c pinout is simple and uses the TO-220 package. There are three pins:
-
Base (B)
-
Collector (C)
-
Emitter (E)
The tip41c and tip42c have the same pinout. This makes it easy to use them in the same socket or board. The base pin controls the transistor. The collector pin goes to the load. The emitter pin goes to ground for tip41c or to positive supply for tip42c.
Tip: Always check the datasheet for the right pinout before wiring. A wrong connection can break the transistor.
Here is a table that compares the main features and uses of both:
| Feature/Aspect | TIP41C (NPN) | TIP42C (PNP) |
|---|---|---|
| Transistor Type | NPN | PNP |
| Maximum Voltage (VCEO) | 100 V | 100 V |
| Maximum Current (IC) | 6 A | 6 A |
| Power Dissipation | 65 W | 65 W |
| Typical Applications | Audio amplifiers, power supplies, switching circuits, voltage regulators, LED drivers, inverter circuits, battery chargers | Similar jobs but in PNP circuits |
| Role in Circuits | Used in NPN setups, often with TIP42C for push-pull or amplifier outputs | Used in PNP setups, matches TIP41C for NPN/PNP pairs |
The tip41c and tip42c are a lot alike in specs. But their polarity and type decide where to use each one. The tip41c is best for NPN circuits. The tip42c is best for PNP circuits.
Substitution Guide
Compatibility
A lot of people think about swapping the tip42c for the tip41c. These two transistors look almost the same, but they do not work the same way. The tip41c is an NPN transistor. The tip42c is a PNP transistor. This means they let current move in opposite ways. The tip41c lets current go from collector to emitter if the base gets a positive signal. The tip42c works the other way. It lets current go from emitter to collector if the base is negative.
If a circuit is made for the tip41c, it needs an NPN transistor. If someone puts a PNP transistor like the tip42c in, the circuit will not work right. The base signal and voltage will not fit. The tip41c and tip42c can handle the same amount of current and power, but their polarity is different. This makes them not good as direct swaps.
Note: Always look at the circuit diagram before picking a replacement. The right polarity is very important for the circuit to work safely.
Circuit Impact
Switching the tip41c with the tip42c changes how the circuit acts. The tip41c turns on when the base is positive. The tip42c turns on when the base is negative. If the wrong type is used, the transistor might not turn on or could cause a short. The current will flow the other way. This can break other parts in the circuit.
For example, in an amplifier, the tip41c helps make the signal stronger by letting more current flow. If someone uses the tip42c instead, the amplifier might not work at all. The resistors and voltage will not be right for a PNP transistor. The current gain will not help if the transistor never turns on.
The table below shows what happens if someone tries to swap these transistors:
| Scenario | Result |
|---|---|
| Using tip41c in PNP circuit | Circuit does not turn on |
| Using tip42c in NPN circuit | Circuit does not turn on |
| Matching transistor to circuit | Circuit works as designed |
| Swapping without changes | May cause damage or failure |
Tip: When looking for other options, always match the transistor type (NPN or PNP) and check the pinout.
Risks
Using the wrong transistor can cause many problems. The most common problem is that the circuit will not work. The tip41c and tip42c need different base-emitter voltages. If a PNP transistor is put where an NPN should go, the base signal will not turn it on. The circuit might use too much current or not work at all.
Other risks are:
-
Overheating: The transistor can get hot if it tries to work the wrong way.
-
Damage to other parts: Wrong current flow can hurt resistors, capacitors, or the power supply.
-
Safety hazards: In power circuits, using the wrong transistor can cause sparks or smoke.
People should always pick the right replacement. If the tip41c is not there, use another NPN transistor with the same current, voltage, and gain. The datasheet gives the best info for finding safe replacements.
Warning: Never swap a tip41c with a tip42c unless you change the circuit. Always use the right type for the job.
Applications

TIP41C Transistor Uses
The tip41c transistor is used in many strong circuits. It helps make sound louder in audio amplifiers for speakers. It can also control motors in toys, robots, and big machines. Engineers use the tip41c in power supplies to keep voltage steady. This transistor can turn on LED groups and act as a switch in digital gadgets. The tip41c is liked because it can handle lots of current, works with high voltage, and lasts long. Both new learners and experts find it simple to use for business or fun projects.
-
Common tip41c uses are:
-
Audio amplifiers
-
Motor drivers for robots and toys
-
LED drivers and lighting systems
-
Power supply regulation
-
Switching circuits for microcontrollers
-
Tip: The tip41c transistor is cheap and easy to put on most circuit boards.
TIP42C Uses
The tip42c is used in similar ways but for PNP circuits. It often works with the tip41c in push-pull amplifier outputs. Many people use it in audio amplifiers, power supplies, and switching circuits that need a PNP transistor. The tip42c can also control motors and run loads when negative voltage is needed. Like the tip41c, it is strong and simple to use.
-
Typical tip42c uses are:
-
PNP side of audio amplifiers
-
Power supply circuits needing PNP transistors
-
Motor control with negative voltage
-
Complementary push-pull stages with tip41c
-
Choosing the Right One
Engineers pick tip41c or tip42c based on what the circuit needs. The biggest difference is polarity. The tip41c is for NPN jobs, and the tip42c is for PNP jobs. Both have close voltage and current ratings. The table below shows how they match up:
| Feature | TIP41C (NPN) | TIP42C (PNP) |
|---|---|---|
| Transistor Polarity | NPN | PNP |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 100 V | 100 V |
| Max Collector Current | 6 A | 6 A |
| Package Type | TO-220 AB | TO-220 AB |
| Complementary Device | TIP42C | TIP41C |
Note: Always use the right transistor polarity for your circuit. This helps the circuit work safely and as it should.
TIP41C Datasheet and Resources
Where to Find Datasheets
If you want to use the tip41c, always look at the datasheet first. The datasheet tells you how the tip41c works and what it can handle. Central Semiconductor is a trusted company. They have the datasheet on their website. You need to make an account to get it. This keeps the file safe. STMicroelectronics is another big company. They also have the tip41c and share product info. Their website often lets you get the datasheet right away. Estartrade-ic has a helpful article about the tip41c. It gives links to datasheets and more technical info. These websites help students and engineers find the right data before building a project.
Tip: Always use datasheets from trusted companies. This helps you avoid mistakes when making your circuit.
Key Specs to Check
Before you use the tip41c in a new project, check some important numbers. These numbers help keep the tip41c safe and working well.
-
Maximum collector-emitter voltage (VCEO): This is the highest voltage the tip41c can take between collector and emitter.
-
Maximum collector current (IC): This shows the most current the tip41c can safely carry.
-
Maximum power dissipation (PD): This tells how much heat the tip41c can let out before it gets too hot.
-
DC current gain (hFE): This shows how much the tip41c can make the input current bigger.
-
Collector-emitter saturation voltage (VCE(sat)): This affects how well the tip41c works as a switch.
-
Thermal considerations: This includes the temperature range and how well the tip41c can cool down.
-
Pinout and base current requirements: This makes sure the tip41c fits in the circuit and works with the control signals.
The table below shows the most important values from the tip41c datasheet:
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 100 V |
| Maximum Collector Current (IC) | 6 A |
| Maximum Power Dissipation (PD) | 65 W |
| Collector-Emitter Saturation Voltage (VCE(sat)) | 1.5 V |
| Operating Temperature Range | 0°C to 150°C |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 15 to 75 |
Note: Always check these numbers. This helps you stop mistakes and keeps the tip41c safe in your project.
TIP41C and TIP42C are not the same type. TIP41C is NPN, but TIP42C is PNP. You cannot swap them in a circuit. Always use the right transistor for your circuit. Check the voltage, current, and pinout before picking one. Look at the datasheet to use it safely. If a transistor stops working, look for blown fuses or shorts. Also check for broken parts. Change any bad parts and keep the transistor cool. Picking the right part and fixing problems keeps circuits safe and working well.
FAQ
Can someone use TIP41C and TIP42C together in one circuit?
Yes, people often use TIP41C and TIP42C together. They work as a pair in push-pull amplifier circuits. This helps make audio amplifiers and power stages work better.
What happens if a person swaps TIP41C with TIP42C by mistake?
The circuit will probably not work right. The current will not move the way it should. This can break other parts in the circuit. Always check the transistor type before you change it.
How can a person tell if a transistor is NPN or PNP?
You can look at the datasheet to find the type. Circuit diagrams show arrows on the symbols. NPN arrows point out. PNP arrows point in. TIP41C is NPN. TIP42C is PNP.
Are TIP41C and TIP42C good for beginners?
Yes, both are simple for beginners to use. Their datasheets are easy to read. The pinouts are not hard to understand. Many starter kits have these transistors. Beginners can use them safely to learn.
Where can someone buy TIP41C or TIP42C transistors?
You can buy these transistors at most electronics stores. Online shops like Digi-Key, Mouser, and Amazon also sell them. Always buy from trusted sellers to make sure you get real parts.
Written by Jack Elliott from AIChipLink.
AIChipLink, one of the fastest-growing global independent electronic components distributors in the world, offers millions of products from thousands of manufacturers, and many of our in-stock parts is available to ship same day.
We mainly source and distribute integrated circuit (IC) products of brands such as Broadcom, Microchip, Texas Instruments, Infineon, NXP, Analog Devices, Qualcomm, Intel, etc., which are widely used in communication & network, telecom, industrial control, new energy and automotive electronics.
Empowered by AI, Linked to the Future. Get started on AIChipLink.com and submit your RFQ online today!




